Use of Artificial Intelligence
A solution to reduce metal artifacts on CT scans has been researched for about fifty years. Although many methods have already been developed to reduce metal artifacts, these methods alone appear to be inadequate. Isala researchers started building a database, developing and training the algorithm two years ago. With that, they investigated whether metal artifacts can be reduced using AI.
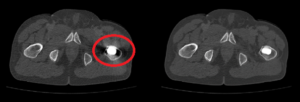
The image shows a CT of a patient’s pelvis. The CT on the left side shows that this patient has metal in the body, a medical implant or prosthesis. The metal gives problems on the scan. It can be seen that the implant radiates like a star, “polluting” the rest of the image. Moreover, the space right around the implant is completely black and hard to analyse.
What challenge does it solve?
An AI algorithm has been developed within Isala Hospital to reduce metal artifacts in CT images caused by metal hip replacements. This greatly increases the image quality. For the first time, the performance of this AI algorithm has been compared with existing techniques for the reduction of metal artifacts in CT images of patients with metal hip replacements. During this testing phase, metal artifacts were significantly reduced by the AI algorithm, making surrounding tissue such as bone and muscle more visible.
How does this AI algorithm work?
A large data set of more than 100,000 images was used to develop the AI algorithm. This dataset includes images with and without metal artifacts. Using these images, the algorithm was trained, and learned when there was an artifact in the image and when there was not. It recognizes the dark and bright stripes, so to speak, and extracts them. In short, the algorithm corrects the image, so the metal artifact is a lot less. This makes the surrounding tissue more visible.
How to proceed?
The first results of this AI algorithm are promising and have already been published in a renowned international radiology journal. It also received the second prize for the “best abstract” at the Dutch Radiologists’ Days. But there is still much work to be done before this AI solution can be deployed in clinical practice. For example, CT images can be distorted by many different metallic implants. It remains to be investigated whether the AI algorithm works for all these different implants.
More information
For further information, contacts or more such projects, contact the Health and Care Working Group. Visit:
- The Community Platform (for participants)
- Or the website page (for non-participants)






